|
Now that the sensor is built it must be able to mate with the process where the measurement is to be made. Generally, this is done using standard pipe threads. This standardizes process and conduit connections and reduces the number of different types of threads used in a plant. For example, a direct immersion sensor assembly for most applications will have a 1/2 NPT thread.
In processes where it is not practical or possible to open the process line to replace sensors, a thermowell is used. The thermowell is permanently installed in the system and a spring-loaded sensor whose length is designed to fit into the thermowell is installed. The sensor length is designed to bottom in the thermowell with a predetermined spring force. This contact increases thermal conductivity to the thermowell and supports the sensing sheath for protection from process vibration. The sensor can now be removed from the thermowell for replacement or calibration without disrupting the process. RdF’s exclusive springload design interaces with all 1/2 NPT hardware, offers failsafe spring loading directly on the end of the probe sheath, and prevents probe rotation due to vibration that can damage connection leads.
Thermowell materials vary from carbon steel to Hastelloy, depending on process fluid and service temperatures. Figure 7 illustrates the three common thermowell mounting configurations: threaded, flanged, and socketweld. Connections between the thermowell and the connection heads are typically made using pipe nipples. The pipe nipple length varies depending on the insulation material requirements and clearances in the plant. It is also common in some applications to use a union/nipple extension which assists installation. The pipe union permits easier removal of the sensor assembly and provides a method for orienting the conduit connection in a particular direction.
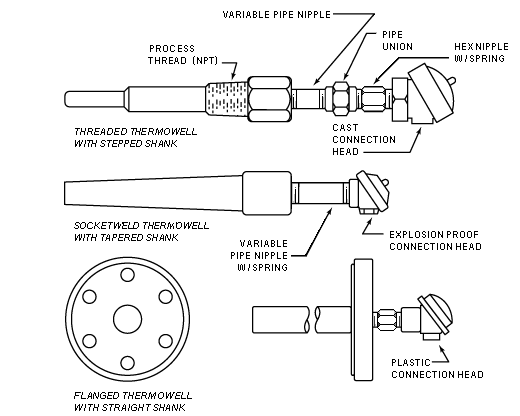 |
| Figure 7. The common thermowell mounting configurations are the threaded, socketweld and flanged thermowell |
Connection heads are generally used as protection for sensor leadwire exit and as a junction point for leadwires going to other instrumentation (readout or control). Connection heads have screw-on covers, internal terminal boards, and female pipe threads for conduit and process connections.
Standard connection heads are usually:
 |
General purpose. Cast iron or aluminum heads with screwed on gasketed covers; designed to withstand normal plant conditions including a washdown of equipment and generally will meet NEMA 4 requirements; standard size is approximately 4 x 4 in. |
| |
|
 |
Explosion proof. Also cast connection heads with screwed-on covers; designed to be used in areas with explosive or combustible materials and often certified by Factory Mutual. RdF’s explosion proof head is smaller than others: approximately 2.75 x 2.75 in. with a custom terminal block leaving good cavity volume and up to eight connection posts to fit most applications. |
| |
|
 |
Specialty connection heads. A variety of plastic or stainless steel connection heads are available for use in sanitary applications or near corrosive processes such as chemical processing for plating.
|
©RdF, 2003, updated excerpts.
Original Publishing: SENSORS, March 1985, AN ADVANSTAR PUBLICATION
|




